Hello, if you have any need, please feel free to consult us, this is my wechat: wx91due
Assignment 2024S1
ELEC9713 Industrial and Commercial Power System
Part A
A power supply system is designed for four groups of loads as shown in Fig.1, where there is one equivalent source at bus 1.
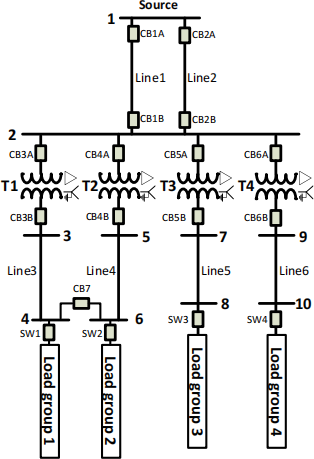
Figure 1 Power supply system for four groups of loads
The ratings of each of two identical lines 1 and 2 are 7.5MVA, 11kV.
The ratings of each of four transformers are as follows:
Transformer T1 : 2.50MVA, 11kV ∆/415V Y;
Transformer T2 : 2.50MVA, 11kV ∆/415V Y;
Transformer T3 : 1.25MVA, 11kV ∆/415V Y;
Transformer T4 : 1.25MVA, 11kV ∆/415V Y.
Each of the four transformers is in wye-connection with neutral conductor at low-voltage side for supplying power to both three-phase loads and single-phase loads.
Transformers T1 and T2 are identical and have the same series impedances.
The ratings of two identical lines 3 and 4 are the same and each of them has a power rating of 2.5MVA and line-line voltage rating of 415V.
The ratings of balanced three-phase loads for each of four groups are given below:
Load group 1: 1.25MVA, 415V;
Load group 2: 1.15MVA, 415V;
Load group 3: 1.10MVA, 415V;
Load group 4: 1.10MVA, 415V.
Besides balanced three-phase loads, there are also single-phase loads for each of four groups.
Each of the lines 3, 4, 5 and 6 is chosen in such a way that the maximum current flowing through each phase is less than that the line can bear.
a) Under the first operating condition, CB3A, CB3B, CB4A, CB4B and CB7 are closed. The loading conditions for each of load groups 1 and 2 are as follows:
Load group 1: IA = 1250 - 100(A) , IB = 1200
- 100(A) , IB = 1200 - 1220(A) , and IC = 1150
- 1220(A) , and IC = 1150 1080(A) ;
1080(A) ;
Load group 2: IA = 920 -80(A) , IB = 900
-80(A) , IB = 900 - 1250(A) , and IC = 945
- 1250(A) , and IC = 945 1090(A) ;
1090(A) ;
Calculate the currents flowing through each of Line 3 and Line 4.
(Marks: 8%)
b) Under the second operating condition, CB3A, CB3B, CB4A, and CB4B are closed while CB7 is open. The loading condition for Load group 1 is as follows: three-phase loads 1.0MW with a power factor of 0.95 lagging; Single-phase loads: 50kVA with a power factor of 0.98 lagging between phase A and neutral; 80kW with a power factor of 0.975 lagging between phase B and neutral.
Calculate the currents flowing through Line 3. Also calculate currents flowing from bus 2 to the delta side of T1. Assume that the voltages at bus 4 are kept approximately at rated one for each phase and phase-A voltage is taken as reference phasor with an angle of zero degree.
(Marks: 8%)
c) Under the third operating condition, CB3A and CB3B are open while CB4A, CB4B and CB7 are closed. The loading condition for each of load groups 1 and 2 are as follows:
Load group 1: IA = 1340 -50(A) , IB = 1300
-50(A) , IB = 1300 - 1290(A) , and IC = 1410
- 1290(A) , and IC = 1410 1120(A) ;
1120(A) ;
Load group 2: IA = 925 - 60(A) , IB = 842
- 60(A) , IB = 842 - 1280(A) , and IC = 900
- 1280(A) , and IC = 900 1140(A) ;
1140(A) ;
Calculate the currents flowing through Line 4 and CB4A respectively. Also calculate the sequence components of these two groups of currents.
(Marks: 10%)
d) Describe lightning protection system for the overhead transmission lines between bus 1 and bus 2. Sketch a diagram to facilitate your description. Assume that line 1 is separated from line 2 and each of them is supported by different poles. They only join together at bus 1 and bus 2.
(Marks: 8%)
e) Design a surge protection at the primary side of each of four transformers and explain how it works. Also add a protective device to the surge protection against potential danger of frequent overvoltage in the system. Sketch a circuit diagram to facilitate your explanation.
(Marks: 6%)
Part B
The single line diagram of a power system supplying power to two groups of induction motors is shown in Figure 2 below. The cable data are given in Table I below.
Table I Per-meter resistance and reactance for three-phase four-wire Cu/pvc/pvc cables with different sizes
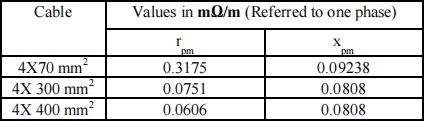
The rated line-line voltage at bus 2 and bus 3 through bus 5 is 400V.
The motors in group M1 are identical, so are motors in group M2. Use the average sub-transient reactance of 25% and a typical X/R ratio of 6 to calculate the impedance of each of the two groups of motors. Treat main DB as open circuit in the fault analysis.

Figure 2 Power system under study
a) Use a power base of 2MVA and a line-line voltage base of 415V at load side to calculate the per-unit Thevenin impedance seen between bus 4 and ground;
(Marks: 8%)
b) Use a power base of 1MVA and a line-line voltage base of 400V at load side to calculate the per-unit Thevenin impedance seen between bus 4 and ground;
(Marks: 8%)
c) Calculate the Thevenin impedances in ohms for both a) and b). Comment on the results;
(Marks: 6%)
d) List down basic criteria when choosing circuit breakers and MCCBs at two sides of bus 2 assembled in a large switchboard or switchgear assembly.
(Marks: 8%)
Part C
1. Figure 3 shows a substation sitting on ground surface which is simplified as a rectangular cuboid with top and side views shown. Four identical rods are adopted for its lightning protection. They are placed at four corners of an isosceles trapezium as shown in Fig. 3. Such a design is also for protecting other devices peripheral to the substation. The rectangular cuboid is placed within the trapezium symmetrically with its two sides overlapping with two sides of the trapezium. The dimensions are as follows: a=12.5m, b=16m, c=8.0m, h1=7.5m, w1=6.0m.
To meet lightning protection level-II requirement, determine the minimum height h of each of four identical rods above the ground using rolling sphere method to protect the substation. Also list down other forming parts in the lightning protection system for the substation.
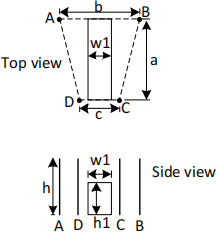
Figure 3
(Marks: 20%)
2. List down the forming components of a roof-top lightning protection system and
component. Discuss how to design an effective grounding system and its role in discuss its other roles.
(Marks: 10%)