CSI 2120
Programming Paradigms
Similarity image search
Comprehensive assignment
(24%)
Winter 2024
Project for a group of 2 students at most
Part 1 due February 16th before 23:59
Part 2 due March 8th before 23:59
Part 3 and 4 due le April 10th before 23:59
Late assignment policy: minus 10%for each day late. For example : a project due Friday night but handed out on the Monday morning: -30%
Problem description
Nowadays, images are created and accumulatedata frenetic pace. It has become essential to have powerful computer tools capable of analyzing these images and facilitating the search, classification, and discovery of images of interest. In this project, you are asked to program a simple method for searching similar images. By similar images, we mean images that resemble each other in terms of the content they present and their visual appearance, colors and textures (for example, images showing sunsets).
Your program will manipulate color digital images. Let's then explain how these images are structured. A digital image is divided into a rectangular grid in which each element is a pixel ('picture element'). This grid contains a certain number of columns and rows, defining the image's resolution (for example, your phone can probably produce images with a resolution of 4032x3024 pixels). A pixel contains the color information associated with the corresponding position in the image. If your image were in grayscale (a 'black and white' image), each pixel would have a value between 0 and 255 (this 8 -bit representation is the most common), with 0 being black, 255 being white and the other values representing different shades of gray. In the case of a color image, each pixel contains three values (three channels), corresponding to the three primary colors: red, green, blue (RGB). These three values represent the amount of red, green, and blue required to produce the desired color. For example, the color 255: red, 255: green, 0: blue will produce a light yellow, while the color 50: red, 0: green, 0: blue will result in a dark red. The values associated with a pixel are usually represented by a vector [R, G, B] containing the values for these three channels (e.g. [255, 255, 0] for light yellow). Since each color can take a value between 0 and 255, the combination of the three channels produces 256 x 256 x 256 different colors (i.e. more than 16 million).
We are looking for similar images. So, let’s assume that images with similar colors should have similar content. This is a simplistic assumption that is not always true but generally yields acceptable albeit imperfect results. This is what we will verify in this project. Therefore, it is necessary to calculate the histogram of animage and compare these histograms.
The histogram is simply the count of the colors contained in an image. It involves counting how many pixels have the color [0, 0, 0], how many have the color [0, 0, 1], and so on. However, this would mean counting the pixels for all 16 million possible colors, which is expensive and not very precise. It is therefore recommended to reduce the color space. This can be done by simply reducing the number of possible values, for example, by going from 8-bit values to 3-bit values per channel, resulting in a color space of only 8 x 8 x 8 = 512 possible colors. In this case, a simple bit right-shift by 8 – 3 = 5 positions reduces the space. The histogram will then have only 512 entries, abin for each of the possible colors. To compare images with different resolutions (different numbers of pixels), it is necessary to normalize the histogram, i.e., divide each entry by the total number of pixels (such that by summing all the values of the histogram, we will obtain 1.0).
Histogram comparison
As explained, the images will be compared by comparing their histograms. This can be done using histogram intersection which can be computed, for the histograms H1 and H2, as follows:
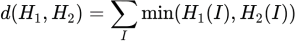
If the two histograms are identical, this sum will give a value equal to 1.0. Conversely, if the two images have no colors in common, then their histogram intersection will be equal to 0.0. Consequently, the more similar are two images, the closer to 1.0 will be their histogram intersection.
Searching similar images
You are asked to find the images that are similar to a query image using color histogram intersection. An image dataset will be provided for the search. The algorithm that searches the K most similar images to a query image I using a color space reduced to D bits is as follows:
1. Compute the reduced color histogram of I
a. Reduce the pixel values by applying (8-D) right bit shifts for each channel R, G, B.
i. R' = R >> (8-D)
ii. G' = G >> (8-D)
iii. B' = B >> (8-D)
b. The number of bins in the histogram H will be N=2D * 3
c. Count how many pixels of each color are contained in I to obtain histogram H. The histogram H is an array of N elements.
i. The index of the histogram bin corresponding to color [R',G',B'] can be computed as (R' << (2 * D)) + (G' << D) + B)
d. Normalize H such that the values of all its bins sum to 1.0
2. Compare H with all pre-computed histograms in the image set.
a. This comparison is done using histogram intersection
b. Returns the K images with distances the closest to 1.0
Programming
You have to write programs under different paradigms that solve different versions of this problem. You will receive specific instructions for each language.
Each program will be marked as follows:
Program produces the correct result [3 points]
Adherence to programming paradigm [2 points]
Quality of programming (structures, organisation, etc) [1 point]
All your files must include a header showing student IDs and names of the group members. All files must be submitted in a zip file.
Dataset
• You have access to a dataset of images. The images are provided in jpg format. The histogram of each image in this dataset has been computed (3 bits per channel) and saved in a text file.
• We also give you 16 query images. You will have to find the 5 most similar images to each query images. The query images are provided in jpg and ppm format, you can use one or the other.
1. Object-oriented part (Java) [6% of your final mark]
Since this solution must follow the object-oriented paradigm, your program must be composed of a set of classes. Specifically, it must include, among others, the classes listed below.
In addition to the source code of your solution, you must also submit a document that includes a UML diagram of all your classes (showing attributes, associations and methods). Do not use static methods, except for the main function. This document must also cite all references used to build your solution.
• The SimilaritySearch class
o that contains the main method
. you must specify the image filename, the image dataset directory
• java SimilaritySearch q01.jpg imageDataset2_15_20
. you can assume that the histograms of the image dataset have been pre-computed
. however, you must compute the histogram of the query image
. you can assume that the search is done on 3-bit color reduced images but make your program as generic as possible (no hard-coding of the depth value except in the main method).
. The program must print the name of the 5 most similar images to the query image
• The ColorImageclass that includes
o A constructor that creates animage from a file
. public ColorImage(String filename)
. you can read the image from the jpg or the ppm format (just choose one format)
• you can use the JMF Java API to read jpg images
• the ppm format is just a text file with the RGB values listed
. the pixel values of the images are stored in an array representation of your choice (to be described in the submitted document)
o The following image attributes (and the corresponding getter methods)
. int width
. int height
. int depth (the number of bit per pixel)
o A getPixel method that returns the 3-channel value of pixel at column i row j in the form of a 3-element array
. public int[3] getPixel(int i, int j)
o A reduceColor method that reduces the color space toa d-bit representation
. public void reduceColor(int d)
• The ColorHistogram class that includes
o A constructor that construct a ColorHistogram instance for a d-bit image
. public ColorHistogram (int d)
o A constructor that construct a ColorHistogram from a text file
. public ColorHistogram (String filename)
o A setImage method that associate animage with a histogram instance
. public void setImage(ColorImage image)
o A getHistogram method that returns the normalized histogram of the image
. public double[] getHistogram()
o A compare method that returns the intersection between two histograms
. public double compare(ColorHistogram hist)
o A save that saves the histogram into a text file
. public void ColorHistogram (String filename)
o plus any other classes, methods or attributes you judge necessary
Rules
You can do this assignment in a group of two to learn team work. Make sure you collaborate both in thinking and brainstorming about this problem and programming with your partner.Any similarity between your programs to other groups is considered plagiarism. Yes, if you do not like teamwork, you can do it alone. Do not use any code or program from the Internet because it is also considered plagiarism.
See the university policies for plagiarism in the following link.
https://www2.uottawa.ca/about-us/provost
Important Note: Using ChatGPT is strictly forbidden, if your TA sees that your code comes from chatGPT it, you will receive 0 for all parts of this project immediately.
Measures that we take to detect plagiarism
Teaching assistants have been instructed to report to the professor any suspicion of plagiarism they find when they mark assignments.
If plagiarism has been detected in any part or in the whole assignment, the professor will take appropriate measures. Recall that it is equally bad to copy a solution and to let someone else copy your solution.